
Let's talk about RFID
This is the first in a series of posts about RFID, hope you enjoy.
Radio-Frequency IDentification, or RFID, is a technology of wireless communication that uses electromagnetic fields and radio waves to remotely store, retrieve, exchange or identify information digitally contained in special devices known as RFID tags. It’s already widely present in our daily lives, like in: access control, contactless payment, inventory control, tracking, anti-theft system and many others.
General infrastructure and components
RFID infrastructures are generally made up of 4 basic components:
- Tag or transponder
- Reader or interrogator
- Middleware or controller
- Management software, host software, enterprise software and etc
Also, the infrastructure as a whole can be classified by the types of tag and reader in use:
- Passive Reader Active Tag (PRAT): Based in a passive reader that only receives radio signals from active tags that are battery operated and only transmit.
- Active Reader Passive Tag (ARPT): Based in a active reader that query passive tags.
- Active Reader Active Tag (ARAT): Based in a active reader that “wake up” active tags when they enter in its range.
Tag or transponder
RFID tags are the devices in the end of the chain, the ones closer to the user, and responsible to identify the object/person who possesses it. It’s general composition is basically the same:
- Microchip, responsible to process requests from the reader and generate the response with the information from the memory.
- Memory, responsible to store the information related to the tag itself, like facility code, site code and card number, and if possible, information about the object that it is attached to, like onwer name, room number, account balance and etc.
- Antenna, responsible to receive and transmit signal waves, while also generating eletricty to the microchip, a physical process discussed later on.
- Battery, when present, helps to power the microchip and boost the transmission range of the tag.
- Protective case, responsible to protect and glue everything together.
The tag itself is not aware of its composition, format or content, nor of its access privileges for the cardholder, being responsibility of the other elements of the system to guarantee and apply it.
Reader or interrogator
The reader is responsible to generate the electromagnetic field that will power up the RFID tags, to interrogate the tags in its range and request the information in tag’s memory, to synchronize the communication process, to receive the response via radio frequency and decode this analog signal into digital and then send this digital signal to the middleware.
Readers are categorized in two types, based in its capabilities: read-only and read-write. As the names suggests, read-only readers are only able to read tag’s memory, while read-write readers are able to read and write tag’s memory (if the tag supports such feature).
As with tags, the reader itself is not aware of the composition, format, content or access privileges of the tag, being responsibility of the other elements of the system to guarantee and apply it.
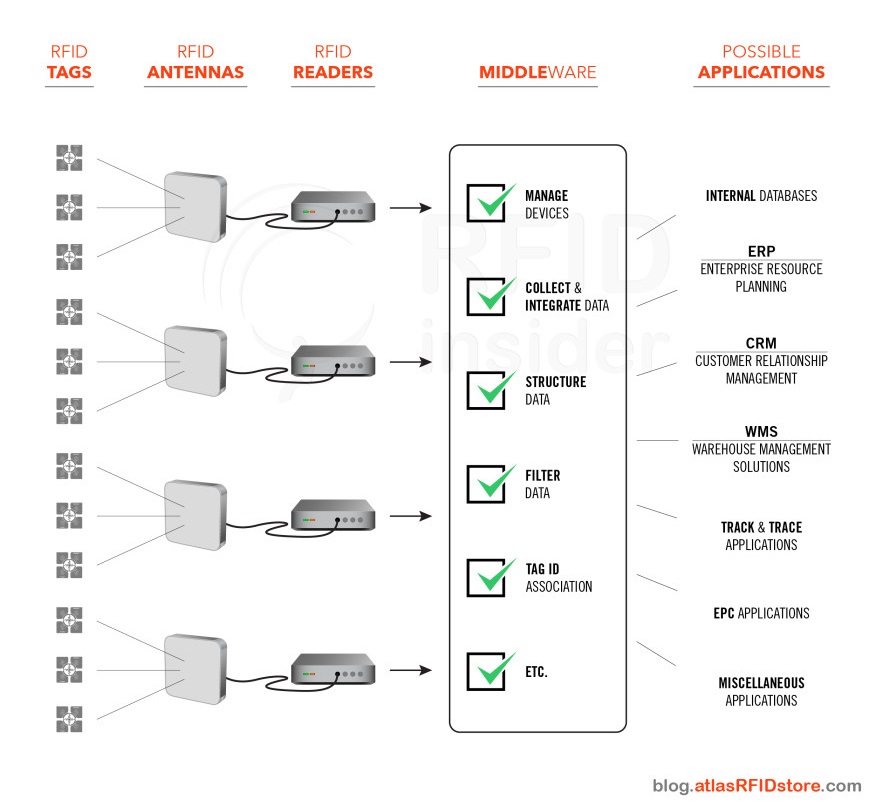
Middleware or controller
Middleware is a generic term used to describe the software that sits between the reader and the management software. It’s a critical component in any medium-to-big RFID infrastructure because it’s the responsible for: control all peripheral devices (tags and readers); mediate the communication between peripherals and management software; abstract different technologies from different readers; decode, format, filter and understand the format of data coming from the reader and some others.
As the first component in the infrastructure that can decode and understand the data coming, it’s the first responsible to check the validity, debug and convert the information received into something that the management software can understand.
It is worth noting, however, that not all RFID implementations would require a middleware. When the number of tags read are high, when the traffic of information is intense or when the high availability of the services that are interacting with the RFID system is essential, then a middleware is desired.
Management software
The management software can be considered the backend of the RFID infrastructure, like databases, management software (WMS, SAP, Microsiga) and others. It’s where the required information to the whole system is stored, managed and queried by the middleware.
References
[1] https://www.atlasrfidstore.com/rfid-insider/6-things-rfid-middleware-can-do-for-you/